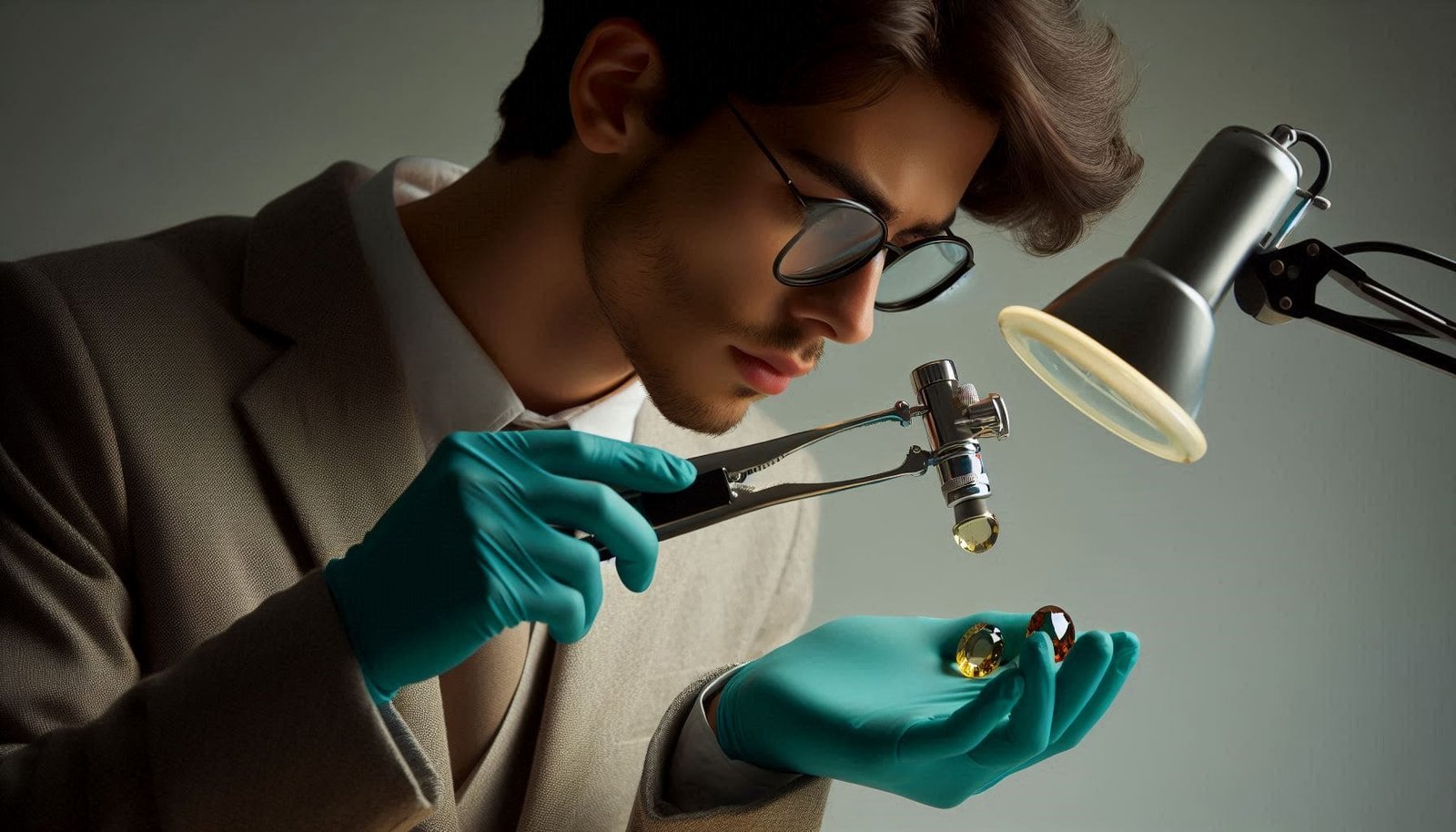
To identify a gemstone, there are a number of very accurate tests. Each gem has physical and optical properties that are constant within narrow limits and, to a certain extent, can be determined. Hardness, gravity, fracture type, cleavage, and inclusion are physical properties of a gem, while R.I., dispersion, and optical character come under optical properties.
Identifying gemstones commences with a visual assessment. These initial characteristics offer the first and most valuable insights. With some basic knowledge of the color, cut, transparency, and optical behavior of a gemstone and a few trusty tools, you can unravel these gemstone mysteries.
Here, we will cover almost all the methods by which an experienced jeweler or geologist identifies the gemstones. So, embark on this adventure with curiosity and confidence, and let the world of gemstones unfold before your eyes!
1) Colour
The color of a gemstone is its first and most prominent sign for classifying the gemstone. By looking at the color, any experienced jeweler or gemologist classifies the gems to some extent at first sight. Observe the hue. Like Ruby, red spinner and some garnet look similar, but if we look carefully, we can easily differentiate between them only through the color.
2) Sharpness of edges
This is the second most crucial aspect of gemstones identification. The hardness of the stone is estimated by looking at the sharpness of the edges, which makes its classification easier.
The gem’s hardness is gauged on the Mohs scale. Diamonds are the hardest at 10, while talc is the softest at 1. This property reveals the gem’s resistance to scratches and wear over time.
3) Optical Character
Certain gems exhibit double refraction, where light splits into two rays. This optical behavior can help differentiate similar-looking stones. To check the optical character of stone, you need a handy polariscope.
4) Dispersion
Some gems scatter light into a beautiful display of colors, known as dispersion. This phenomenon is particularly striking in diamond identification.
5) Inclusions and birthmarks
Inclusions are like the gem’s birthmarks, unique to each stone. They offer a peek into the gem’s formation history and authenticity. To check this out, you will need a 10x lens. This is the most important tool for the identification of gemstones. This handy tool helps you closely inspect the gemstone. It is not very expensive, and you can buy it and keep it with you.
(Other Observations)
Apart from this, some other aspects are also paid close attention to correctly identify a gemstone; these mainly include:
A) Transparency
Transparency refers to the presence of any internal imperfections, such as inclusions or blemishes. whether it’s clear, slightly hazy, or completely opaque.
B) Luster
The gem’s sparkle, or play of light, is a result of its luster. This feature gives gems their captivating shine, which can vary from glassy to silky to metallic.
C) Cut and shape
The cut of a gemstone affects its overall appearance. Shapes can range from classic round to emerald and princess cuts. Pay attention to the facets.
D) Cleavage and Fracture
A gemstone is always formed within a certain crystal structure. How a gemstone breaks or fractures can reveal its crystal structure. Some gems split along specific planes, revealing smooth surfaces when broken.
Remember
A simulant may be:
Natural; Synthetic; Imitation; Composite; Reconstructed or surface-modified

 Blue Sapphire (Neelam Stone)
Blue Sapphire (Neelam Stone) Yellow Sapphire (Pukhraj Stone)
Yellow Sapphire (Pukhraj Stone) Cats Eye Stone (Lehsunia)
Cats Eye Stone (Lehsunia) Gomed Stone (Hessonite Garnet)
Gomed Stone (Hessonite Garnet) Manik Stone (Ruby)
Manik Stone (Ruby) Moonga Stone (Coral)
Moonga Stone (Coral) Panna Stone (Emerald)
Panna Stone (Emerald) Pearl Stone (Moti)
Pearl Stone (Moti) Citrine Stone (Sunela)
Citrine Stone (Sunela) Iolite Stone (Kaka-Neeli)
Iolite Stone (Kaka-Neeli) Natural Zircon
Natural Zircon Opal Stone (Doodhiya Pathar)
Opal Stone (Doodhiya Pathar) White Sapphire (Safed Pukhraj)
White Sapphire (Safed Pukhraj) Turquoise Stone (Firoja)
Turquoise Stone (Firoja) Amethyst Stone (Katela)
Amethyst Stone (Katela) Rudraksha
Rudraksha Sphatik
Sphatik Pearl Mala
Pearl Mala